Last Updated on March 10, 2025 by Bisma Sehar
The critical infrastructure sectors that serve as the backbone of our nation face continuous and growing cybersecurity threats. In recent months, there has been a noticeable increase in attacks targeting vulnerabilities in internet-accessible operational technology assets across sectors such as energy, water, and transportation.
To strengthen the resilience of these indispensable services against an evolving threat landscape, robust cybersecurity standards and vigilance are required. This article provides an in-depth guide to one of the foremost authorities on critical infrastructure protection, the NERC CIP cybersecurity reliability standards.
Table of Contents
Understanding NERC CIP Standards and Objectives
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) cybersecurity standards are specifically designed to ensure the security of the Bulk Electric System across North America.
These guidelines provide a crucial line of defense against threats looking to disrupt the integral services that rely on a stable power grid. With the increasing sophistication of malicious actors, adherence to NERC CIP standards becomes significantly more crucial.
Recent Cybersecurity Threats to Critical Infrastructure
In recent months, critical infrastructure sectors have seen a significant uptick in cyber attacks attempting to exploit security weaknesses in operational technology systems connected to the Internet.
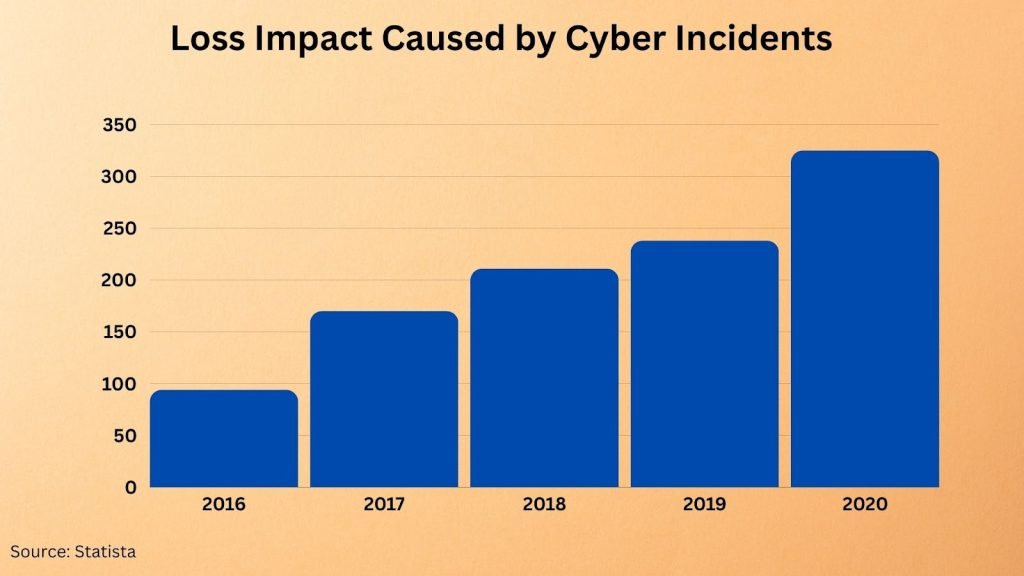
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued multiple warnings regarding this increasing malicious activity from threat actors ranging from cyber criminals to nation-state groups. These alerts emphasize the need for enhanced security measures and standards, such as NERC CIP, to strengthen defenses.
Examples of concerning activity include the following:
- In May 2021, CISA released an advisory detailing a series of intrusions by advanced persistent threat actor Berserk Bear into US pipeline companies. The threat actor gained access to OT networks and appeared positioned to trigger disruptive effects.
- Between January and July 2022, a Russia-linked group called Sandworm conducted reconnaissance on OT assets in sectors like oil and natural gas, electrical, water, aviation, and critical manufacturing. The activity signaled intentions to disrupt critical systems.
- Ransomware continues posing major risks, with groups like Hive extorting $40 million from media giant MediaNews Group after encrypting OT systems and demanding huge payments.
These incidents and trends underscore the severity of risks to essential services and emphasize why standards like NERC CIP are so crucial. Hardening security postures, maintaining vigilance, and improving incident response capacities can help companies better thwart attacks.
Synergies Between NERC CIP and Other Cybersecurity Frameworks
NERC CIP standards have strong synergies with best practices promoted under other cybersecurity frameworks as well, like the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. CISA actively advises critical infrastructure owners and operators to align their security controls with NERC CIP while also implementing complementary best practices.
This integration results in a more robust defense strategy with overlapping safeguards across various standards and guidelines.
Challenges in Implementing NERC CIP Standards
Despite the valuable security benefits, implementing NERC CIP standards can prove challenging even for sophisticated organizations. The complexity of systems that support critical services means security teams must gain deep visibility and implement controls that balance both reliability and protection.
Meanwhile, the threat landscape continues to rapidly evolve with new attacker tools, techniques, and vulnerabilities emerging constantly. Maintaining compliance as risks evolve demands substantial resources and diligence.
Best Practices for NERC CIP Implementation
To address common challenges in implementing NERC CIP, organizations should focus on best practices such as:
- Conducting regular cybersecurity risk assessments informed by the latest threat intelligence to gain visibility into gaps and prioritize remediation based on real-world attacks. Both internal and external assessments are advised.
- Promoting tighter collaboration between IT and OT teams through cross-training, unified risk management, and consistent communication channels. Breaking down silos is key.
- Developing and drilling detailed cybersecurity incident response plans that outline roles, strategies for containment, eradication steps, communication flows, and more. Drills validate readiness.
- Investing adequately in modern security tools, systems, and personnel to keep pace with the volume and complexity of threats while maintaining rigorous standards.
- Pursuing compliance milestones ahead of the deadline to avoid last-minute risks and issues. Building lead time allows more flexibility in addressing problems.
Proactive critical infrastructure companies also go beyond baseline NERC CIP compliance, continuously improving their defenses and response capabilities against a morphing threat landscape. They integrate related standards and best practices to create defense-in-depth.
The Future of NERC CIP
Although current NERC CIP regulations provide a strong foundation, the future promises continuous evolution to address emerging risks. We can expect a greater emphasis on protecting supply chains through the vetting of vendors and third-party partners as well as broadened definitions around what constitutes critical cyber assets.
Future developments in NERC CIP are expected to prioritize visibility across operational technology (OT) environments, real-time monitoring, advanced persistent threat detection powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning, as well as dark web monitoring.
FAQs
The key challenges typically include managing the complexity of operational technology environments, costs associated with continuously advancing security programs, and difficulty balancing reliability with strict compliance with all regulations.
Strategies include conducting regular risk assessments informed by the latest threat intelligence, closely tracking updates to standards, investing in skills and technology proactively, and going above and beyond baseline requirements whenever possible.
Potential implications range from mandatory remediation and oversight to major regulatory fines in extreme cases of negligence. But more importantly, non-compliance elevates the risk of successful and damaging cyber attacks on critical infrastructure.
Conclusion
As threats to critical infrastructure continue to grow in frequency and impact, standards like NERC CIP serve an integral role by mandating baseline cybersecurity best practices across sectors providing indispensable services that society relies upon.
While achieving and maintaining compliance brings formidable challenges, a proactive security approach can help owners and operators meet essential reliability standards while also safeguarding operations from evolving risks.
By adhering to guidelines like NERC CIP and incorporating emerging best practices, critical infrastructure companies can fulfill their duty to deliver resilient and secure essential services.
















