Last Updated on February 13, 2025 by Bisma Sehar
A wastewater treatment system is a practice that combines a variety of unconventional technologies to address specific wastewater treatment requirements.
Treatment of wastewater is rarely a silent process. A wastewater treatment system uses a number of technologies from anaerobic filtration to digital water meters that are designed to manage and withstand fluctuations in treatment requirements will go a long way toward avoiding costly replacements/grades on the road.
Method changes in infection and flow fluctuations in water chemistry demand artificial measures modifications, which an adequate and well-designed wastewater treatment system should be able to handle.
As a water technology booster, prospective adjustments in water effluent requirements.
Table of Contents
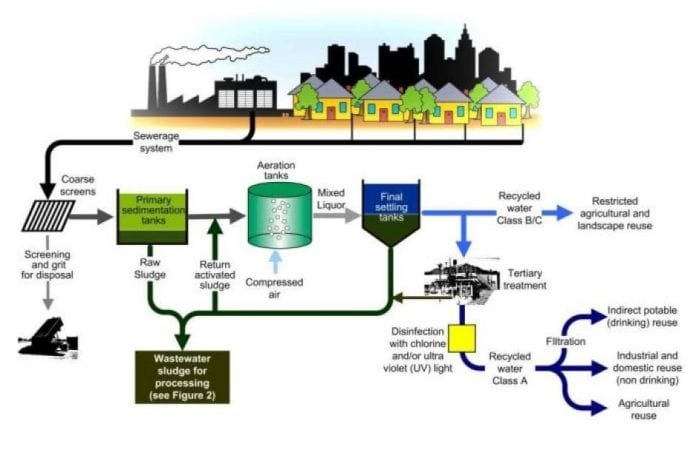
How does a wastewater treatment system work?
Definite treatment processes diversify, but a common wastewater treatment equipment process will usually include the following steps:
Coagulation
Coagulation removes dissolved particles and other pollutants from the body by attaching different chemicals to a reaction container.
This procedure begins with a set of mixing reactors, usually one or two, that add certain chemicals to combine all of the finer particles in the water into heavier particles that settle out.
Flocculation
When the coagulation process is finished, the water is pumped into a flocculation cell, where the coagulated particles are gradually combined with long-chain polymers, resulting in visible, settleable shreds that look like snowflakes.
Sedimentation
The gravity settler (or sedimentation phase of the wastewater treatment process) is a circular device in which flocculated particles and water flow into the chamber and circulate outwards.
The water rises to the peak and overflows at the clarifier’s perimeter in a gradual settling process, allowing the solids to drop to the bottom and form a sludge.
Blanket:
The solids are then raked into a cylindrical tube in the clarifier centre, where they are slowly mixed, and the sludge is pumped out of the bottom into a sludge-handling or dewatering process.
Filtration
Most of the time, the water is pushed via gravity sand filters.
These filters are two to four feet of finely crushed silica sand with serrated edges that are visible.
Sand is frequently deposited in the filter at a depth of two to four feet, where it compacts tightly.
As the feedwater goes through, the particles are trapped.
A packed-bed weigh system is used on smaller mechanical systems with a weight multimedia filter that may be preferable to force sand filtering.
Disinfection
Following the water’s passage through the gravity sand filter, disinfection or chlorination is usually performed to kill any microorganisms present.
This procedure is rarely performed before filtration to disinfect and maintain the filters.
Distribution
If wastewater is recycled in an industrial setting using water technology, it is usually tapped into a holding tank and used as needed.Different water flow meter types are also used.
If the treated water is intended for public consumption, it is frequently piped into a circular distribution system that includes water columns and different collection and distribution forms.
Apart from this, if you are interested to know more about What you need to Know about a Bamboo Weighted Blanket then visit our Home Improvement category.